What is Teeth Whitening Light
Teeth whitening light is a technology used to enhance the effectiveness of teeth whitening treatments. The basic concept involves using a specific type of light, often in conjunction with a whitening agent, to accelerate the process of removing stains and discoloration from the teeth. This method is commonly employed by dentists in professional settings, but some home-use kits also incorporate similar light-based technologies. The light is believed to activate the whitening agent, causing it to break down stains more efficiently and thus speed up the overall whitening process. The ultimate goal of this process is to brighten the teeth and provide a more aesthetically pleasing smile for the individual.
Types of Teeth Whitening Lights
Several types of teeth whitening lights are used in the cosmetic dentistry industry, each utilizing different technologies to achieve the desired results. The choice of light often depends on the specific treatment being administered, the dentist’s preference, and the patient’s needs. These lights typically emit specific wavelengths designed to interact with the whitening agents and the tooth enamel. Different lights have different advantages, such as the intensity of the light and the wavelengths emitted which impacts the overall effectiveness of the whitening procedure. In addition to the technology itself, it’s essential to consider the safety aspects and any potential side effects these various lights can cause, ultimately making sure the patient is getting the best possible results.
LED Teeth Whitening Lights

LED, or Light Emitting Diode, teeth whitening lights are a popular choice due to their energy efficiency and relative safety. LED lights emit a blue light spectrum, often preferred in professional and at-home whitening kits. The blue light specifically interacts with the whitening agent, usually hydrogen peroxide, to accelerate the oxidation process that breaks down stains. LED lights generate minimal heat, making them a comfortable option for patients. Also, they are known for their ability to target specific wavelengths, offering effective whitening with a reduced risk of causing sensitivity or other adverse effects. Their efficiency and safety contribute to their widespread use in cosmetic dentistry, making them a practical solution for those looking to brighten their smiles.
Laser Teeth Whitening Lights
Laser teeth whitening, in comparison to LED, uses a concentrated beam of light to enhance the whitening process. Lasers provide a more intense light source, which can speed up the reaction of the whitening agent, resulting in quicker whitening effects. The precision of lasers allows dentists to target specific areas of the teeth, which can be beneficial in cases of localized staining. The laser method, however, usually requires strict safety precautions, and the intensity of the light necessitates careful use. The laser method is typically conducted in a professional dental setting, ensuring optimal control and safety throughout the whitening treatment. The powerful nature of lasers means that this technique should be administered by qualified professionals.
UV Teeth Whitening Lights
Ultraviolet (UV) lights, sometimes used in teeth whitening, are powerful and require special caution. UV light can effectively activate the whitening agents, accelerating the stain removal process. However, UV lights are associated with a higher risk of potential side effects, including increased sensitivity and damage to soft tissues. Due to these risks, UV light whitening is less commonly used compared to other methods like LED and laser. Professional settings employ strict protective measures to reduce exposure risks, which includes both the patient and the dentist. The use of UV lights demands meticulous care and expertise to ensure safety, making it critical to thoroughly consider the potential hazards.
The Science Behind Teeth Whitening Lights

The science behind teeth whitening lights involves photochemical reactions, which is the process that light initiates a chemical change. When the specific wavelengths from the light source interact with the whitening agent, typically hydrogen peroxide, it speeds up the breakdown of stains. The light energy activates the peroxide molecules, causing them to release oxygen free radicals. These unstable molecules then penetrate the enamel and dentin, breaking down the stain molecules into smaller, less visible particles. The efficiency of this process depends on several factors, including the type of light, the concentration of the whitening agent, and the duration of exposure. The light serves as a catalyst, significantly improving the bleaching effects, allowing the teeth to appear noticeably brighter within a shorter time frame.
How Light Activates Whitening Agents
Light, in the context of teeth whitening, functions as an activator, boosting the efficiency of the whitening agents. Different types of light, such as LED and laser, emit different wavelengths, and these wavelengths are tailored to interact optimally with the chemical compounds in the whitening gel. The light energy is absorbed by the whitening agent, exciting the molecules and accelerating their reaction. This leads to a more effective release of oxygen molecules, which break down the stains on the teeth. Without light activation, the whitening agent works more slowly. The use of light can dramatically increase the speed and effectiveness of the whitening process, resulting in more impressive results, often in a shorter timeframe. The interaction between light and the whitening agent is crucial for enhanced teeth whitening.
The Role of Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the active ingredient in most teeth whitening treatments, including those that use light. The compound acts as an oxidizing agent, breaking down the stains that cause discoloration. When activated by light, hydrogen peroxide releases oxygen molecules that penetrate the tooth enamel. These oxygen molecules then react with the stain molecules, breaking them down. The concentration of hydrogen peroxide varies in different whitening products, with higher concentrations typically found in professional treatments. Light plays a pivotal role in speeding up the whitening process by maximizing the effectiveness of hydrogen peroxide. The light’s energy boosts the hydrogen peroxide’s stain-removing capabilities, leading to brighter and whiter teeth.
The Process Step by Step

The teeth whitening process using light typically involves a few key steps. First, the dentist will assess the patient’s teeth and determine the appropriate treatment plan. The process is then initiated by cleaning and polishing the teeth. Following this, a protective barrier is applied to the gums to prevent irritation from the whitening agent. The whitening gel, which contains hydrogen peroxide, is applied to the teeth. Next, the light is directed at the teeth, activating the gel and accelerating the whitening process. The light exposure is typically done in intervals, with the gel reapplied between sessions. The total time for the procedure can vary, but usually, it takes about an hour. Post-treatment, the dentist will provide aftercare instructions to maintain the results and minimize any potential side effects.
Preparing for the Treatment
Preparation for teeth whitening with light begins with a dental check-up and cleaning. The dentist will assess the overall health of your teeth and gums. If there are any underlying issues, like cavities, these should be addressed before whitening. The teeth are professionally cleaned to remove plaque and surface stains, which enhances the whitening treatment. Discuss any sensitivity or concerns with the dentist beforehand. Also, the dentist will determine the shade of your teeth to monitor the whitening progress. This preparation phase ensures that the teeth are in optimal condition for the procedure and that the patient is well-informed about the process and expected outcomes. Following these steps can maximize the effectiveness of the whitening treatment.
Applying the Whitening Gel
Applying the whitening gel is a critical step in the teeth whitening process with light. A protective barrier is first placed on the gums to prevent irritation from the whitening agent. The gel, which contains hydrogen peroxide, is then carefully applied to the surfaces of the teeth. The dentist ensures that the gel is evenly distributed to maximize its effectiveness. The gel’s concentration varies depending on the treatment and the patient’s needs. The application process is meticulously done to ensure that all visible areas of the teeth are covered. The dentist may apply multiple coats of the gel during a single session to achieve the desired result. This careful and professional application is essential for the successful and safe outcome of the teeth whitening procedure.
Using the Light for Activation
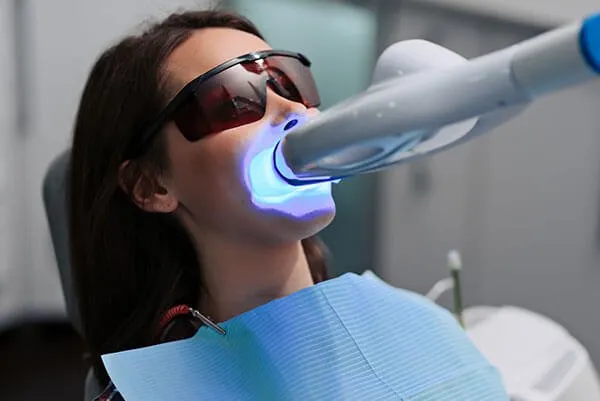
Using the light for activation is the core component in the teeth whitening process. Once the whitening gel is applied, a specific type of light is directed at the teeth. The light’s energy accelerates the process by which the hydrogen peroxide breaks down the stains. The duration of light exposure is carefully controlled, typically lasting for a few minutes per application. The light is strategically positioned to ensure even coverage and maximum activation of the gel. Dentists usually apply the gel and use the light in intervals, repeating the process to achieve the desired level of whiteness. This methodical approach ensures optimal results while minimizing the risk of complications. Proper light activation is key to the success of the whitening procedure, leading to a brighter and more attractive smile.
Aftercare Tips for Best Results
Aftercare following teeth whitening is important for maintaining the results and preventing new stains. Avoid foods and drinks that can stain teeth, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and dark-colored berries, for the first few days. Smoking should be avoided as it can quickly discolor the teeth. Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice daily and flossing regularly. Use a toothpaste designed to maintain the whiteness and consider using a whitening mouthwash. Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings to keep your teeth healthy and bright. Following these steps can help you enjoy the benefits of your teeth whitening for an extended period, keeping your smile radiant and beautiful.
Maintaining Your Bright Smile
Maintaining a bright smile after teeth whitening involves several strategies. Continue with the aftercare tips, especially avoiding staining foods and drinks. Use a whitening toothpaste and mouthwash regularly, which can help to remove surface stains. Consider touch-up treatments as recommended by your dentist to maintain the whiteness, typically once or twice a year. Maintain good oral hygiene with regular brushing and flossing to prevent new stains and keep your teeth healthy. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also essential, as your dentist can assess your teeth and offer advice on maintaining your bright smile. By following these practices, you can extend the life of your whitening treatment and preserve your stunning smile.
Addressing Sensitivity After Whitening

Teeth sensitivity is a common side effect after teeth whitening, but it can be managed effectively. Use a desensitizing toothpaste containing potassium nitrate before and after the treatment. Avoid extremely hot or cold foods and drinks for the first few days. Consider using a fluoride rinse, which can help strengthen the enamel. If the sensitivity is severe, consult your dentist, who may recommend additional treatments. Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage discomfort. Usually, sensitivity subsides within a few days or weeks. It is important to remember that sensitivity is temporary. Following these steps can provide relief and help you enjoy the results of your teeth whitening treatment.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Teeth Whitening Lights
Teeth whitening lights, like any cosmetic procedure, have potential risks and side effects. The most common side effect is teeth sensitivity, which can range from mild to moderate. Gum irritation or inflammation can occur if the protective barriers are not properly applied. Excessive use of the light or high concentrations of the whitening agent can potentially damage the enamel. Rare but possible side effects include changes in the tooth structure or uneven whitening. It’s essential to consult with a dentist to assess your individual risk factors and discuss any concerns before undergoing the treatment. Choosing a qualified dentist ensures that the procedure is performed safely. Understanding these potential risks enables patients to make informed decisions about their dental health.
Who Should Avoid Teeth Whitening Lights
Not everyone is a suitable candidate for teeth whitening with lights. People with sensitive teeth or gum disease should consult their dentist before treatment. Individuals with existing dental work, such as fillings, crowns, or veneers, should be aware that the whitening treatment will not change the color of these restorations. Pregnant or breastfeeding women are usually advised to avoid the procedure. Children and teenagers are generally not recommended to undergo teeth whitening. Anyone with severely stained or discolored teeth might not achieve the desired results, and alternative options should be considered. Consulting a dentist is crucial to determine if teeth whitening is right for you. They can provide guidance based on your oral health.
Alternatives to Teeth Whitening Lights
If teeth whitening lights aren’t suitable for you, several alternatives can enhance your smile. Over-the-counter whitening products, like strips and toothpastes, can gradually lighten the teeth. Professional teeth whitening, without light activation, is another option, although the results might take longer to appear. Dental veneers or bonding can cover and improve the appearance of severely stained or discolored teeth. Regular dental cleanings can remove surface stains and maintain the natural brightness of your teeth. Lifestyle changes, like reducing coffee, tea, and smoking, can also prevent stains. Consider your personal dental health needs and expectations and discuss them with your dentist, who can recommend the most effective alternative to achieve the desired results.
